Sunday, July 31, 2011
Data Operators
If x = True Then ' Compares x to the Boolean value True.
' Insert code to execute if x = True.
Else
' Insert code to execute if x = False.
End If
There are five Boolean operators that can be used to manipulate TRUE/FALSE values. These operators have the following meanings, where x and y represent values of TRUE or FALSE.
Tuesday, July 26, 2011
Data Types- Integers
The purpose behinde integers are that they provide the finest preformance for a 32-bit processor as well as those integral types which are slower to load and store both from and to memory
It is possible to covert integer data types to others however this process can be done without encountering a System.OverflowException error.
Thursday, July 21, 2011
Selection and Repetition
(you may need to research algorithms in google.
Use the word “if” ie If red then ……)
1. Moving through a set of traffic lights.
When driving the car and going through a set of light you have three options :
If green light keep going. if yellow light start to slow down and if red light brake and stop
2. Deciding whether to take an umbrella to school.
If the forecast has said rainy and it has been raining on previous days then take umbrella becasue there's a high chance of wet weather if the weather is sunny and bright then don't take umbrella to school. If it is cloudy and sunny pack your umbrella in your bag.
3. Giving a student an A, B or C on their test.
Calculate the students marks and then compare to the criteria available then determine the students marks from there
Often an algorithm will often require you to repeat a task in order to solve a problem; when this is done in an algorithm the structure is called repetition.
1. Adding the correct amount of cordial to water to make a drink.
Get jug of water and pour cordial into jug and repeat until its to your prefrence of taste
2. Filling a bucket with water.
Fill bucket upto rim if over flows tip some water out and refill to the rim making sure that the water doesnt over flow if so then repeat process
3. Blowing up a balloon.
Algorithms
1. boil the water,
2. place coffee in the cup,
3. place sugar in the cup,
4. add the boiling water,
5. add milk,
6. stir.
1. Examine the algorithm above. What two properties of the algorithm enable it to correctly describe the solution to the problem of making a cup of coffee? What is it that makes an algorithm correct?(Hint: what would happen if you swapped step "6" and step "2"?)
In order for the algorithm to work, you need all the correct steps like the above algorithm for making coffee. It is impossible for step 6 and step 2 to be swapped around because after adding the hot water there is nothing to stir and and if you add the coffee last it probably wouldn't dissolve as it hasn't been stirred and the sugar would also just sit at the bottom of the cup.
It any of the steps were put in order or missing you wouldn't come to the solution of mixing the coffee or being able to make one.
2. Define Algorithms for the following processes.
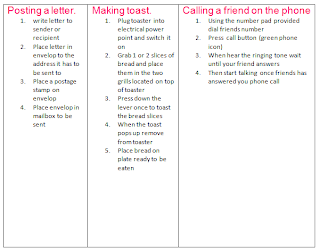
Tuesday, July 19, 2011
Flowchart Basics
- A flowchart is a organised graphic representation of a logic sequence the purpose of a flow chart is to provide people with common reference points when working with a process/project
- The basic flowchart symbols for the following are:
- Computational steps or processing function of a program: Shows process/ steps throughout flow chart and is the most used symbol
- Input o
r Output operation: Data which is available for input or resulting from processing
- Decision Making and Branching: Shows question or or branch in the process flow. Usually the symbol is used when there is 2 options available

4.
Sunday, July 3, 2011
MY WEBSITE


